In Alberta there are currently two Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) : the YYCIX in Calgary and the YEGIX in Edmonton. These IXPs allow networks to interconnect directly, rather than through one or more (international) third party networks.142 The advantages of a direct interconnection are primarily related to cost, latency, bandwidth, and network resiliency.are “interchanges” where networks can connect to other networks without having to go through a third-party provider. Technically, they are the physical infrastructure through which ISPs and content delivery networks (CDNs) exchange internet traffic127.
The key advantages of an IXP include128:
- Improving performance: shorter network distance, better latency
- Increasing resiliency: reduced congestion, stopping cyberattacks
- Accessing global content: improved performance to major content providers
- Reduced costs: transit costs to third-party providers is lower
- Domain Name System (DNS) resolution resilience: offers multiple paths to top level domain DNSs
Many IXPs are operated by non-profit organizations or by a consortium of ISPs, to provide a neutral site where all participants and the network traffic can be treated equally. In Canada, as of March 2021, there are 12 IXPs in operation, including two in Alberta129.
Table 6. CIRA List of IXPs in Canada in 2021130.
CITY | IXP | METRO POPULATION | WEBSITE |
Toronto | TORIX | 5,928,040 | |
Montreal | QIX | 4,098,927 | |
Vancouver | VANIX | 2,463,431 | |
Calgary | YYCIX | 1,392,609 | |
Ottawa-Gatineau | OGIX | 1,323,783 | |
Edmonton | YEGIX | 1,321,426 | |
Winnipeg | MBIX | 778,489 | |
Halifax | AIXP / HFXIX | 403,390 | |
Saskatoon | YXEIX | 295,095 | |
Moncton | AIXP / MonctonIX | 144,810 | |
Saint John | AIXP / SJIX | 126,202 | |
Charlottetown | AIXP / PEIX | 69,325 |
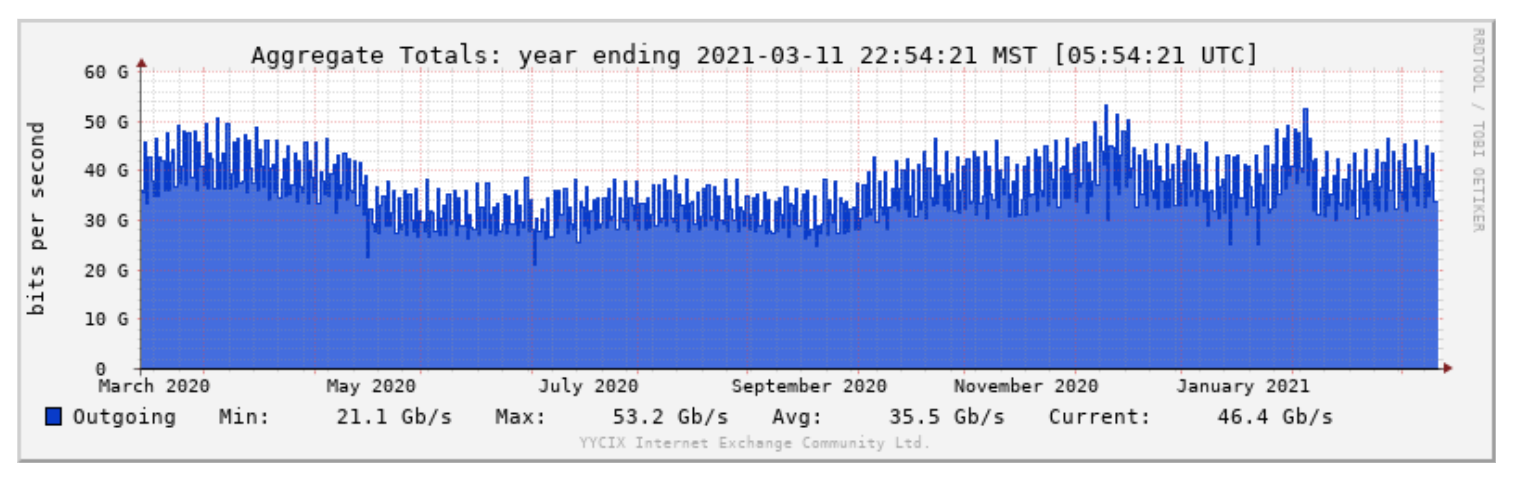
Alberta’s Internet Exchange Points (IXPs) are the YYCIX in Calgary and the YEGIX in Edmonton. The YYCIX was introduced in 2013 and has 24 71 peers, transferring 27035.65 Mbps5 Gbps, on average (Figure 1219). The YEGIX was created in 2015 and currently only has two open connections, with six more scheduled to connect.
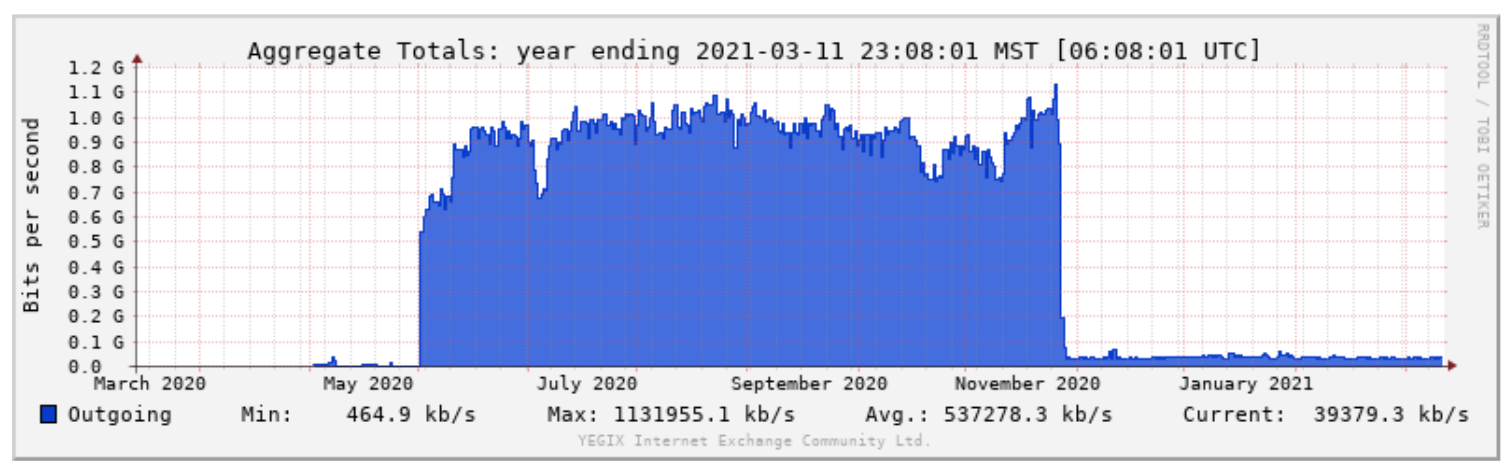
has 10 peers, transferring 537 Mbps, on average (Figure 20).
Figure 19Figure 12. Aggregate total traffic of YYCIX in the year ending 13 July 2016143
March 11, 2021131.
Figure 20Figure 13. Aggregate total traffic of YYCIX YEGIX in the week ending 13 July 2016144 March 11, 2021.
The YEGIX traffic load over the 2020-21 year is quite disproportionate, with loads over 1 Gbps from June to December. This is not unusual, as the YEGIX Network Manager explained to this report author: “a simple change of route metric at a peer can steer a lot of traffic toward or away from the IX.” This underscores the robustness to which IXPs must be scaled.As a result of the internet exchanges in Calgary and Edmonton, Tier 1 ISP Hurricane Electric now peers in both IXs. Hurricane Electric advertises transit fees starting at $0.32 USD/Mbps/month145 (before transport and data centre fees). It is of note that while Hurricane Electric’s internet is advertised on a per Mbps fee, it is only available for purchase in increments of 1,000 Mbps.
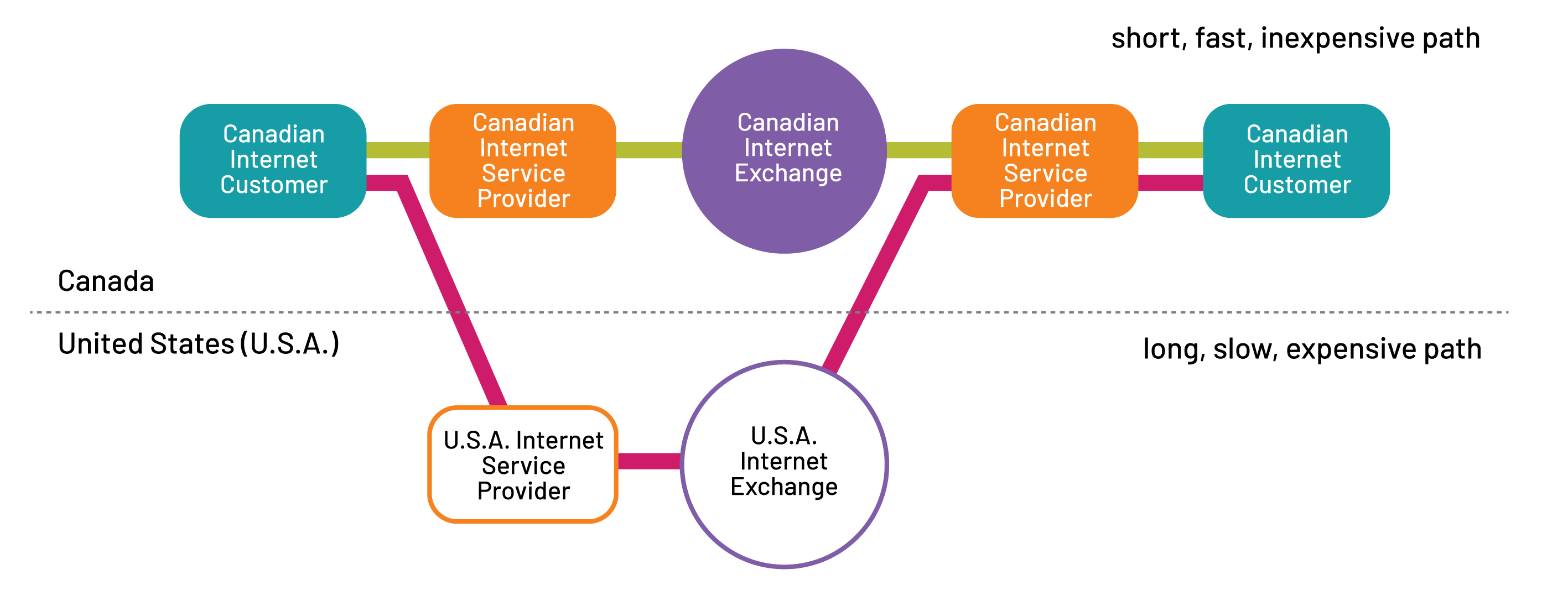
A connection to a local IXP may allow regional ISPs to transfer data without limit or cost, vastly improving the connection speed between customers of two adjacent ISPs. A direct interconnection also avoids the need for data to travel through other cities or continents in order to move from one network to another, thus reducing latency and keeping local traffic local (Figure 1421).
Figure 21 Figure 14. The network paths to connect two Canadian internet customers through a Canadian IX (green) and an American IX (redpink)146 .
According to Packet Clearing House, “a strong domestic Internet exchange point Exchange Point is the first and most critical component of a cyberwarfare defense”147 defense133.” This is because countries without an Internet Exchange IX are heavily dependent upon on international data circuits for their domestic connectivity. In the case of the 2007 cyberattacks on Estonia, denial-of-service attacks were halted at the country's internet exchange and IX, which meant they had minimal impact on domestic internet traffic. The Canadian Internet Registration Authority considers Internet Exchanges to be an essential component of internet infrastructure, and promotes Internet Exchange development across the country. CIRA encourages government IT departments to facilitate Internet Exchange development and improve the Canadian internet landscape by working closely with Internet Exchanges
In 2014, the Internet Society created a Mutually Agreed Norms for Routing Security (MANRS) initiative to bring basic security to internet routing. There were three primary issues to resolve: route hijacking, IP address spoofing, and route leaks. In 2017 alone, there were 14,000 internet routing issues. In 2018, the Internet Society expanded MANRS to include IXPs, to further strengthen security for global routes134.
The benefits of peering to an IX for governments include network resiliency. If a government’s internet service provider ISP is taken offline by a denial-of-service attack, the government can lose connectivity to the whole of contact with its citizenry. However, if the government’s internet service provider its ISP peers at Internet Exchange Pointsan IXP, then its services will remain available to its citizens by virtue of the connections to other internet service providers in that Internet Exchange.
ISPs.
The Government of Alberta required Bell to enable a peering point at Alberta’s IXPs for the use of SuperNet customers, should they request it, within the most recent SuperNet contract (signed in July 2018).
References
127Wikipedia. Internet exchange point - Wikipedia. 18 February 2021. Accessed 11 March 2021.
128CIRA. Canada’s Internet Exchange Points | CIRA. Accessed 11 March 2021.
129CIRA. Canada’s Internet Exchange Points | CIRA. Accessed 11 March 2021.
130CIRA. Canada’s Internet Exchange Points | CIRA. Accessed 11 March 2021.
131YYCIX. Graphs, 11 March 2021. Accessed 11 March 2021.
132YEGIX. Graphs, 11 March 2021. Accessed 11 March 2021.
References
142. Wikipedia. Internet Exchange Point article. Accessed 17 May 2016.
143. YYCIX. Graphs, 13 July 2016. Accessed 13 July 2016.
144. YYCIX. Graphs, 13 July 2016. Accessed 13 July 2016.
145. Hurricane Electric. Internet Services. Accessed 12 June 2016.
146. Woodock, B. and Edelman, B. Towards Efficiencies in Canadian Internet Traffic Exchange, 2012. Packet Clearing House for the Canadian Internet Registration Authority. Accessed 14 June 2016.
147. 133Stapleton-Gray, R. and Woodcock, B (Packet Clearing House). ACM Queue. National Internet Defense—Small States on the Skirmish Line - Attacks in Estonia and Georgia highlight key vulnerabilities in national Internet infrastructure, 19 January 2011. Accessed 29 July 201611 March 2021.
134Security Week. Internet Society Calls on IXPs to Help Solve Internet Routing Problems. 23 April 2018. Accessed 11 March 2021.